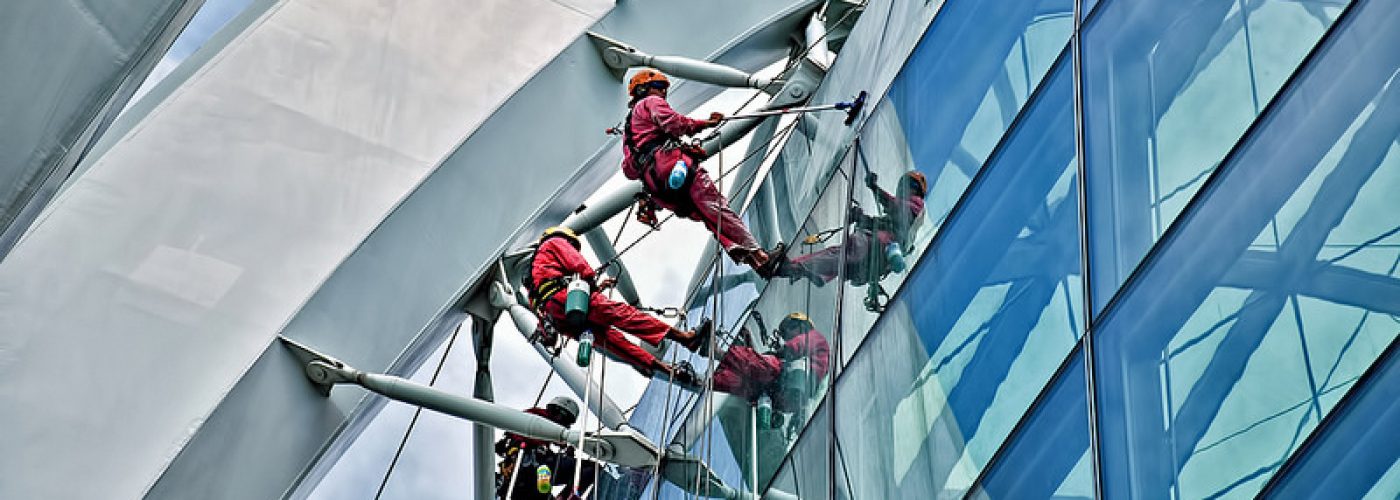
As we move towards a more sustainable economy, our goals have rightly shifted, as has our long-term ambition. With the latest development in window technology revealing the potential to cut cleaning costs and a reduction in heating bills, it is unsurprising to see builders, architects and estate managers eagerly eyeing the true benefits of “smart windows”. Believed to be on track to hit the market within five years, University College London (UCL) has produced a prototype that confirms three major benefits.
Firstly, the windows offer “self cleaning”. It accomplishes this by being ultra-resistant to water, the material making any moisture hitting its surface form spherical droplets that roll away. As they do so they pick up dirt along the way, removing dust, debris and other contaminants. This is achieved through a conical design; a pencil-like nanastructure etched on the glass which enhances the smart window’s abilities by trapping air and thus allowing only a small amount of water to settle on the surface. This is in comparison to traditional glass which allows rain to settle on the surface and stay there, leaving streak marks as it rolls away.
Crucially, the glass also saves energy. Utilising a tiny layer of low-cost vanadium dioxide the glass is capable of stopping thermal radiation from escaping during cold periods preventing heat loss. Meanwhile, when the season changes, the glass stops sunlight radiation penetrating the building. The value and size of vanadium dioxide makes it ideal and a better, more sustainable option over other glass coatings like silver or gold based layers. UCL believes it will enable the glass to help reduce heating costs by up to 40%.
In addition, the structure offers anti-glare capabilities – dramatically cutting light reflection internally – that has been estimated to have the anti-reflective capabilities of moths and such creatures that have evolved to evade predators.
Dr Ioannis Papakonstantinou, UCL project leader, noted the innovative characteristics of the smart window calling the product a “self-cleaning, highly performing” piece of technology. Discussions are currently underway with glass manufacturers in the UK. Key ambitions going forward involve scaling up the nano-manufacturing methods.