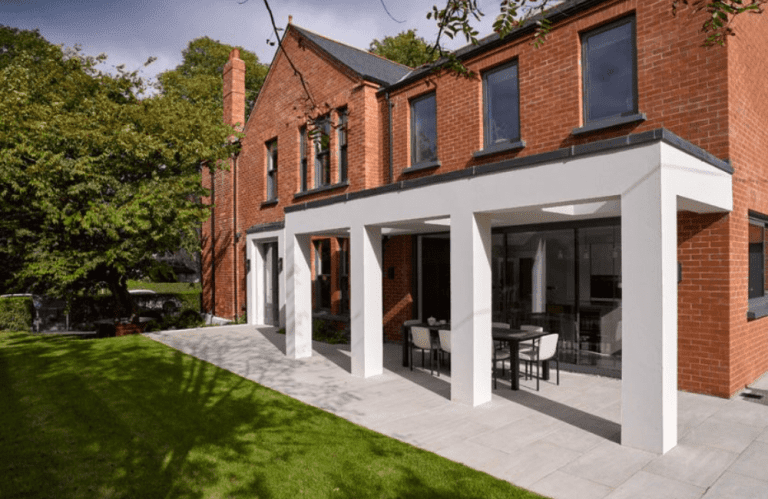
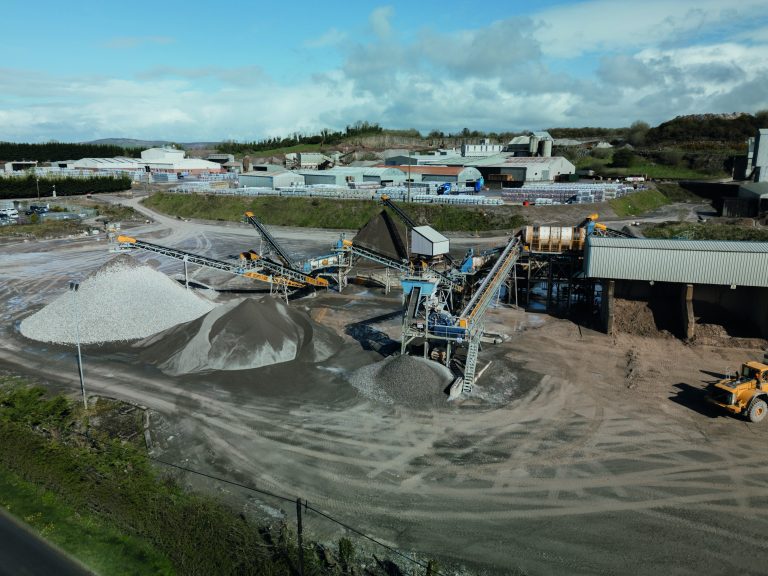
Marshalls has launched Modal X™, a lower-cost, lower-carbon alternative to granite paving, offering high durability, design flexibility and straightforward installation. Building on the company’s popular Modal collection, which launched in 2020, the new Modal X features eight colourways, smooth and textured finishes, fifteen plan sizes and five depths, including three complementary sett sizes with a textured riven surface. Additionally, Marshalls’ market-leading Priora® paving is incorporated into the range, providing permeable options. The breadth of the Modal X range gives landscapers and their customers flexibility when developing mixed-use spaces including pedestrianised zones and high traffic areas. Different paving formats, such as modern linear units, help customers delineate spaces. At the same time, smaller elements can be used for finer detailing and edging, creating character and unique design elements. Likewise, Modal X offers a broad palette of warm, neutral and complementary colours, including a captivating pink granite, silver grey and light cream granite. This enables landscapers to create a contemporary finish that is aesthetically pleasing and hard-wearing. Modal X is crafted using Marshalls’ MaxiMix® Technology. This innovative technology produces an inseparable bonded layer, ensuring colour permanence and robust protection against the elements. Further, the patented surface technology creates a superior blend of aggregates and binders, resulting in an exceptionally durable, resilient paver, which is highly resistant to UV fading. Modal X is also ideal for budget-focused projects as it can be laid on a flexible, unbound bed requiring lower-priced materials, reduced installation time, and in turn, the labour costs, versus granite options. “While budgets are tightening, customers still want clever, creative and beautiful spaces,” said Tom Foster, Trading Director at Marshalls. “Our new Modal X range gives landscapers true design flexibility with hundreds of options and combinations, plus ease of installation and help towardreduced labour costs.” Modal X is the first new product range to be produced by the company’s innovative dual block plant in St Ives, Cambridge, which brings significant advantages in sustainability, lead times and bespoke ordering. “Our new dual block site delivers nearly double the output of a single plant, which is hugely beneficial to customers,” said Simon Magleave, Group Manufacturing Director at Marshalls. “As well as allowing us to cater for large-scale projects quickly, we can use the plant for smaller, morebespoke runs of made-to-order Modal X options with just-in-time delivery. “The dual block plant is partly powered by renewable energy sources, including solar array, plus a new state-of-the-art curing system which reduces carbon impact and speeds up drying times. We’ve also decreased the volume of water and cement used in the production.” For more details on Modal X, visit marshalls.co.uk/modal-x Building, Design & Construction Magazine | The Choice of Industry Professionals