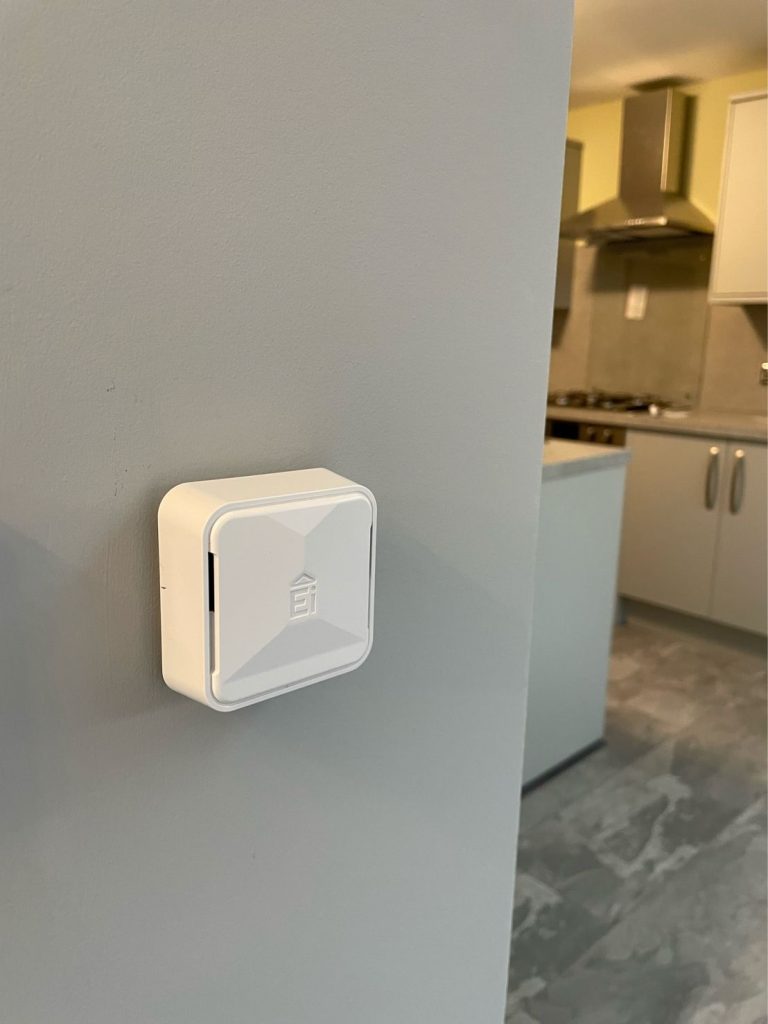
Social return on investment project uncovers the value of IoT sensors to social housing tenant’s health and wellbeing. The University of Exeter has partnered with Aico|HomeLINK and housing industry partners, UK Housing Associations’ Charitable Trust (HACT) and Coastline Housing, for a first-of-its-kind guide and toolkit to realise the social value of Internet of Things (IoT) connected sensors. In recent years, there has been a marked shift in environmental sensor system adoption to create “smart social homes” among registered social housing providers looking to implement a more proactive strategy to identify housing issues early, rather than wait until regulation forces action. Until now, no project has developed a guide and toolkit to evaluate the societal benefits that stem from homes equipped with sensor systems. Entitled “Sensor systems for healthier social housing – A guide or understanding and evaluating the social value or indoor environment sensor systems”, the guide and toolkit aim to support informed decision-making and include establishing connections between housing and health, understanding societal value from using sensor systems, a social return on investment (SROI) forecast, templates and case studies. The toolkits have been collaboratively developed by Housing Associations with experience of sensor systems. Poplar HARCA is one East London Housing Association that has already recognised the practical benefits of smart connected home IoT sensors. Its use of Aico|HomeLINK sensors provides residents and Poplar HARCA with data that helps them to identify issues in their homes, including damp and mould monitoring, ventilation, fuel poverty and indoor air quality. Designed to gather data on indoor environmental conditions, the IoT smart home connected devices are installed in each resident’s home to measure temperature, carbon dioxide, humidity and other factors, to mitigate issues arising from problems such damp and mould, and poor or insufficient ventilation. Launched in May 2023, during the first five months of this 12-month research project, the University of Exeter developed a working logic model. This was informed by Aico|HomeLINK expertise to map out inputs, such as humidity levels, and HACT’s Social Value Insight tool, specifically designed for social housing, to map out the outcomes, such as reduced condensation. The logic model will identify what changes need to be made early in order to improve an indoor environment, such as opening windows or improving the use of heating to reduce condensation and potential hazards from mould. The team has found that sensor systems are valued by housing associations for being able to pinpoint the specific changes in housing conditions more clearly. One example of sensors in use is identifying and proactively fixing a leak in a tenant’s roof. This could prevent risks associated with damp and mould, such as respiratory illnesses, thanks to earlier resolution. This, in turn, would reduce the unaccounted public health issues and poor conditions that may be associated with social housing conditions, particularly for underprivileged and vulnerable groups. Emma Bland, Associate Professor in Environment, Health and Wellbeing at University of Exeter Medical School, concluded: “This technology has the potential to deliver organisational benefits in social housing. However, there is a lack of understanding about the broader social value gained from such systems, and the best practice for adoption. This project builds on many years of research including the groundbreaking Smartline project which focused on more than 200 social households across six years and will strengthen existing and foster new partnerships between University of Exeter, the social housing sector, and the sensor industry.” Chris Jones, Chief Executive Officer for Aico|HomeLINK, explains: “The quality of housing has a profound and tangible influence on residents’ health and well-being. During winter, cold conditions could result in damp and mould, both of which can have a massive impact, such as triggering allergic reactions, and exacerbating asthma and other respiratory infections. By using smart connected home sensors, social landlords can enhance their delivery of safer, healthier and more sustainable homes. These sensors provide both the residents and landlords with valuable data and customised insights, enabling them both to proactively enhance the health and safety of their living spaces.” To find out more about Aico’s HomeLINK Connected Home Solution, please visit: www.aico.co.uk/homelink Building, Design & Construction Magazine | The Choice of Industry Professionals