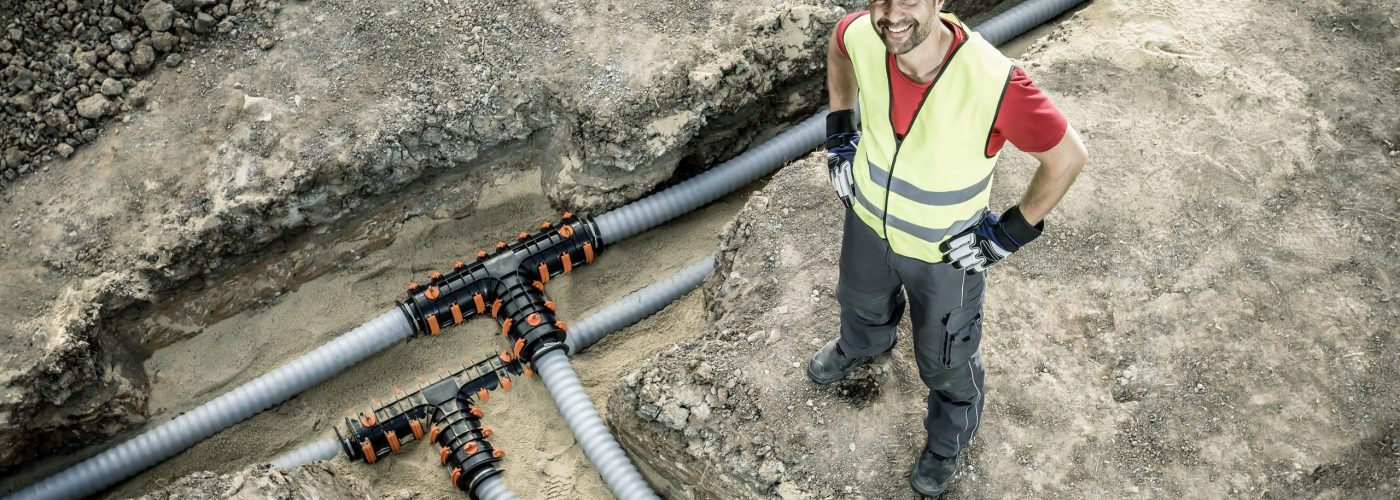
The publication of the new CIBSE/ADE CP1 (2020) Heat Networks Code of Practice is a welcome step in increasing the uptake and quality of design, installation and operation of low-carbon heat networks in the UK, says polymer pipework specialist REHAU.
The long-awaited revision was developed by the Chartered Institution of Building Services Engineers (CIBSE) and Association for Decentralised Energy (ADE), and takes into account the trend toward low-carbon heat networks since the previous guidance was published over five years ago.
Specifically, CP1 (2020) recommends a maximum flow temperature of 70°C on new schemes, encouraging specifiers and contractors to consider fourth generation heat networks. These networks, which typically favour low-carbon heat sources like heat pumps and waste heat, are suited to polymer pipework. The guidance goes on to describe how these pipework solutions can also play a major role in the implementation of district heating schemes across the UK.
With renewable heat networks increasing in popularity as a means of decarbonising buildings in line with Government net zero emissions targets, CP1 (2020)’s messaging comes at a crucial time, says Steve Richmond, Head of Marketing and Technical at REHAU Building Solutions, a leading district heating pipework supplier.
He says: “We have long asserted that the implementation of district heating schemes will be vital to the decarbonisation of the country’s building stock, and are therefore pleased the latest CP1 guidance shares this view. In particular, the guide’s highlighting of the benefits associated with polymer district heating pipework, like lower installation costs and the lack of expansion loops required, clearly demonstrate the key role they will play in reducing emissions.
“We also welcome the guide’s practical recommendations around fitting polymer pipework. This includes highlighting their compatibility with specialist installation methods like horizontal direction drilling, and how compression sleeve joints reduce the potential for failures during installation.”
CP1 (2020) also provides a series of checklists and a toolkit for verifying compliance to ensure quality assurance and regulations within the heat network market, and more detailed guidance on diversity calculations. Taken alongside funding initiatives like the Heat Networks Investment Project and its 2022 replacement, the Green Heat Networks Scheme, Steve is confident CP1 (2020) will ensure new district heating schemes are as efficient and futureproofed as possible.
He concludes: “Government support is helping increase uptake of district heating schemes, and through following guidance like CP1 (2020), heat network providers will be able to more effectively maximise carbon savings while increasing efficiency through reduced heat losses. We view these efficient, low-carbon heat network solutions as instrumental to constructing carbon-neutral new-build properties ahead of the Future Homes Standard introduction.
“As ADE members, we work closely with CIBSE and are fully committed to our role in the delivery of efficient low carbon heat networks. Along with Government policies and funding, CP1 (2020) marks a fantastic turning point in favour of renewable heat networks as one answer to the low-carbon transition, and we are hugely excited to be part of this revolution.”
For further information on REHAU’s pre-insulated pipework systems, and their use in renewable heat pump and district heating networks, visit: www.rehau.uk/districtheating.